Harvard Business Review
Introduction
How do new entrants in consumer product industry rise?
- Distribution
- Advertising
Digital technologies like digital cookies, content-curation websites (Reddit, BuzzFeed) and content-sharing websites (Slideshare, LinkedIn, Medium) lead to a new level of self-expression of individuals. Thus companies can better understand customers’ decision journey and subsequent word-of-mouth.
Digital Marketing landscape:
- Paid Media: TV commercial and Google Ads
- Owned Media: Official Websites
- Earned Media: Influncial customers, word-of-mounth
- Review Websites: Lyft…
Digital Marketing Framework:
- Outbound Marketing: company -> customer —> Search Enginee Maerketing (SEM)
- Inbound Markeying: customer -> product and service —> Search Enginee Optimization (SEO)
- Social Media: customers create contents
- Mobile Technology: the way customers search for and biut products and services
Outbound Marketing
Search Ads
Search Enginee Maerketing (SEM) - To create search advertisement:
- Keywords: what keywords? How much to bid per keyword? Total budgeting?
- Design Search Ads
- Rank higher in the result page
- Prepare land page
Buying Keywords
- The Same Theme
- Different Demographic (Languages)
- Misspellings and Typos
- Rule out negative/unrealated words
Branded Keywords
Bid on one’s own brand - to defend against competitors
Generic Keywords
generic and category keywords
Paying for keywords
Golden Triangle - Upper left
Cost-Per-Click (CPC) bid
Google uses the “generalized second-price auction”, which is based on the extension of the Nobel-prize winning research of Willian Vickery, where the highest bidder get the first ad position but pays the bid amount of the second bidder, who in turn get the second place but pays the bid amount of the third-highest bidder, and so on. Research shows that this mechanism leads to “truth telling” whereby advertisers bid the maximum amount on the basis of their own willingness to pay.
- The top position != The most profitable
- CTR descrease with a lower position, but the conversion rate may increase because consumers who click on links at lower positions implicitly express higher interest in those companies.
- Continuous testing, measurement, and analytics -> find the best position
Quality Score
Factors:
- Potential CTR of an ad
- Relevence to consumers
- Quality of the landing page
Assesing the Effectiveness
Matrics used for search ads:
| Site | Media | Impressions | Clicks | Applications Completed | Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Conversion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . | . | . | |
| MSN | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| SuperPages | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Yahoo | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Unified Marktplace | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Total | . | . | . | . | . | . |
- [Brand Awareness] Impressions (Impr.): Each time your ad shows on a search results page or other site on the Google Network, an impression is counted. Impressions are most important if your goal is to raise brand awareness.
- Clicks: When someone clicks your ad, a click is counted. Clicks can help you understand how well your ad appeals to people who see it. Relevant ads are more likely to receive clicks.
- [Traffic] Click-through Rate (CTR):
CTR=Click/Impression(Impression: # of times seen by consumers) - Convertion Rate:
Convertion Rate = Applicationc Completed / Click - Cost per Click (CPC):
CPC = ost / Click - Search Ad Profit =
(impressions x click-through-rate x conversion rate x margin) - search ad cost - [ROI] Return of Investment (ROI):
ROI = Profit / Cost
Supplemental Reading: Use data to optimize your search campaigns
Display Ads
- Banner Ads
- Insertitial Ads: capture greater user attention but also more intrusive
- Expandable Ads: banner ads that automatically expand to a large portion
Impact: Bannner < Expandable < Insertial
Display Ads Industry
- Content Publishers: e.g. New York Times, small blogs
- Ad Networks: e.g. AdSense by Google (aggregate supply on multiple advertising space and optimally place ads on various websites)
- Ad Exchange: e.g. Rubicon (automate the matching between advertiser and publishers i.e. a programming buying using real-time biding ~ “RTB”)
Assessing the Effectiveness of Displayed Ads
2 ways to buy displayed ads:
- Based on Impressions, using the Cost Per Thousand Impressions (CPM) matric. The Goal is to build brand awareness or brand image
- Based on Clicks. The goal is to maximize clicks and conversion rates.
Measurements:
Same as search ads, CTR and Conversion Rate
- CPM display ad profit = impressions [(click-through-rate conversion rate * margin) - cost per thousand impressions or CPM/1000]
- CPC display ad profit = impressions * click-through-rate x [(conversion rate x margin) - cost per click] …Facebook
Video Ads
- Digital platforms like Youtube or Facebook
- Smart TV and streaming devices like Hulu
Formats on Youtube:
- Skippable in-stream ad: before/during/after the main video
- Non-skippable in-stream ad: 15-20 seconds
- Bumper ad: non-skippable, 6 seconds
Measure the effectiveness
CPM
Social Shares (only on digital platform)
Post-view engagement (only on digital platform)
Impressions
Completed views
Sales !!!
Measuring the Effectiveness of Outbound Marketing
Correlations versus Causation
- Online advertising cause an increase in sales?
- Corellate clicks and sales?
Too mant factors -> Need experiments
Attribution
Influnce in different stages of a purchase decision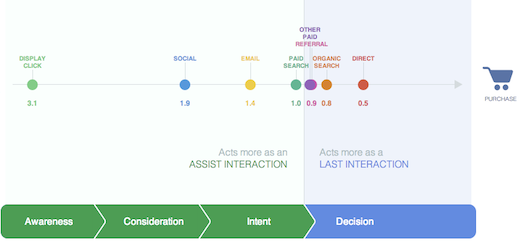
Source: Google Adwords
Advertising channels (like display ads and search ads) do not work in isolation. The attribution model need to take their interaction into account.
Extented reading of models: Google Analytics
Dynamics (Delayed Impact of Advertising)
How to measure long-term effects?
Factors change over time
Ignoring dynamic or long term effects -> Underestimate ROI by up to 40%
Dynamic effects are stronger for search ads than display ads
Online-Offline Interation
Key challenges:
- Interation or potential synergy between online and offline marketing: Costomer base purchase dicsions on both online and offline information. Offline shopping -> personal fit and real-life experience.
- Assessing the impact of online marketing on offline marketing and vice versa (also called omnichannel shopping)
Need to plan together!
Omnichannel Shopping
Different distribution channels (retailers)
Online ads -> offline shopping
Customer Lifetime Value
CTR (click-through-rate) and CPI (cost per install)?
-> Long-term paying customers?
Online customers are more price sensitive and like to shop around -> lower retention rate -> lower CLV
Focus on the CLV (customer life value) to evaluate the effetiveness of digital campaigns, and change the budget allocation to various advertising channels.